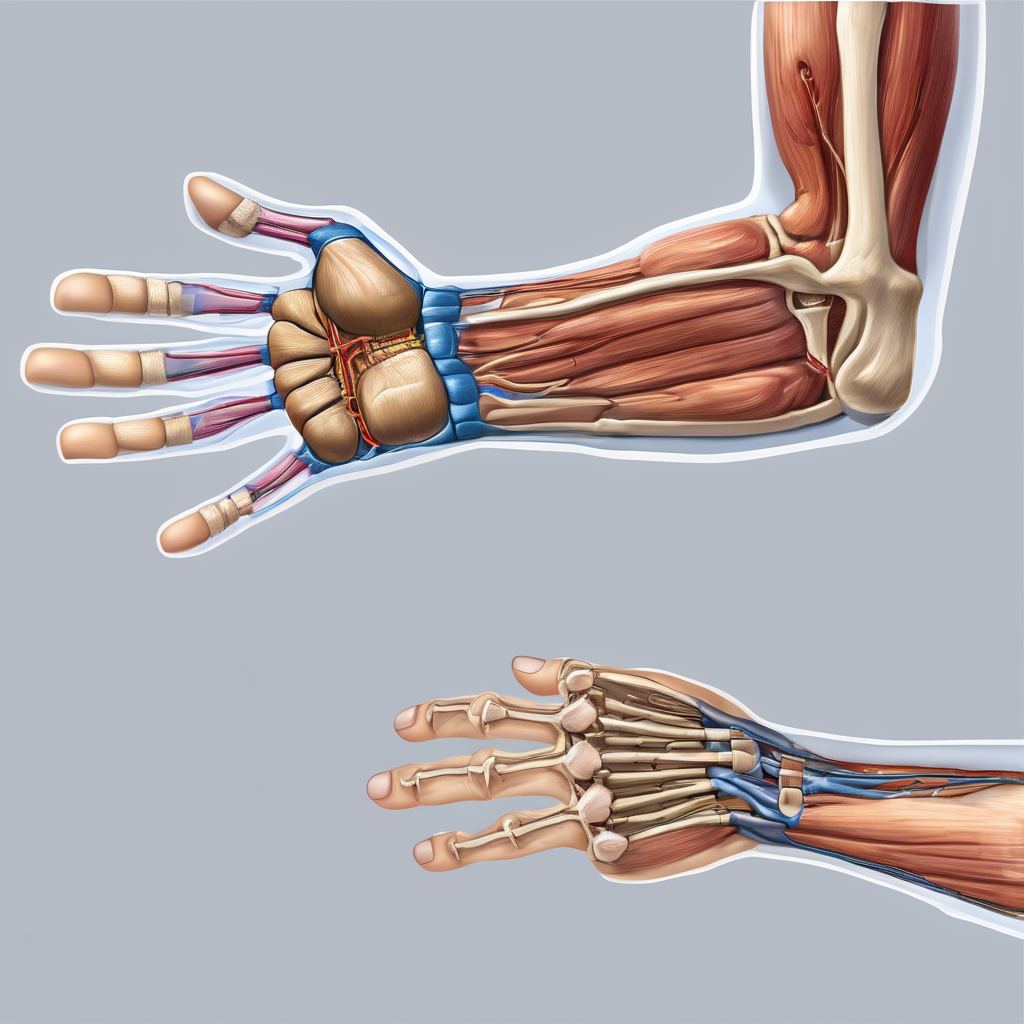
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a medical condition that arises due to compression of the median nerve as it travels through the wrist at the carpal tunnel. The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway on the palmar side of the wrist, formed by bones and ligaments. The median nerve, which controls sensation and movement in the thumb and fingers, is responsible for providing feeling and sensation to the palm, thumb, and three of the five fingers. Compression of this nerve can lead to numbness, tingling, and other symptoms in the hand and arm.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are various factors that contribute to the development of CTS. These can include repetitive motions, such as typing or using vibrating tools, as well as certain health conditions like diabetes or thyroid disease. The following are some common causes and risk factors for CTS:
- Repetitive motions or overuse of the hands and wrists
- Health conditions like diabetes, thyroid disease, or rheumatoid arthritis
- Genetic predisposition or family history
- Poor work ergonomics or incorrect posture
- Previous injuries or trauma to the wrist
Symptoms
The symptoms of CTS can vary, but often include numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the hand and fingers. These sensations may radiate up the arm or be confined to the hand and fingers. Other common symptoms of CTS include:
- Weakness or clumsiness in the hand, making it difficult to perform tasks
- Dropping objects due to weakness or numbness in the hand
- Shocking or burning sensations that travel up the arm
- Numbness or tingling that worsens at night or with certain activities
- Pain or aching in the wrist, forearm, or hand
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing CTS typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies (NCS). Treatment options for CTS range from conservative to surgical interventions, depending on the severity of the condition. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Wrist splints or orthotics to immobilize the wrist and reduce pressure on the median nerve
- Physical therapy to stretch and strengthen the wrist and hand
- Medications to reduce pain and inflammation, such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Surgical release of the transverse carpal ligament to relieve pressure on the median nerve