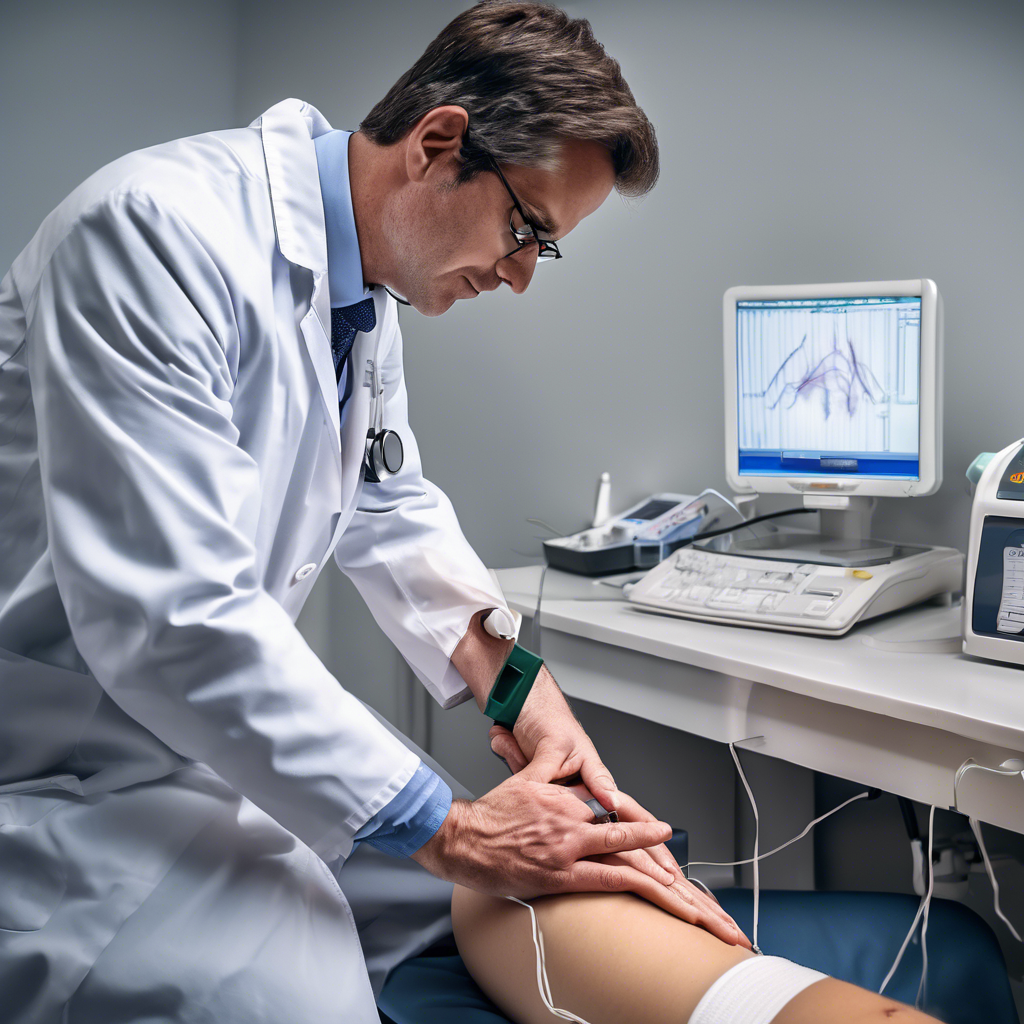
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that affects the hand and wrist, causing numbness, tingling, and pain. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. Diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome typically involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history, and diagnostic tests.
Medical History
To diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome, a doctor will often start by taking a detailed medical history. This includes asking questions about the patient’s symptoms, such as when they started, how long they last, and what activities make them worse. The doctor may also ask about any underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to the symptoms. Some of the factors that may be considered in the medical history include:
- Previous injuries to the wrist or hand
- Underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or arthritis
- Occupational or recreational activities that involve repetitive hand or wrist movements
- Family history of carpal tunnel syndrome
Physical Examination
A physical examination is also an important part of diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome. The doctor will typically perform a series of tests to assess the patient’s hand and wrist function, including:
- Tapping on the wrist to see if it produces a tingling sensation in the hand
- Bending the wrist up or down to see if it causes numbness or tingling
- Testing the strength of the hand and fingers
- Checking for any swelling or tenderness in the wrist or hand
Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, diagnostic tests may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome or to rule out other conditions that could be causing the symptoms. Some of the tests that may be used include:
- Nerve conduction studies, which measure the speed and strength of electrical signals in the median nerve
- Electromyography (EMG), which measures the electrical activity of the muscles in the hand and arm
- Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, to rule out other conditions that could be causing the symptoms
Treatment and Management
Once carpal tunnel syndrome has been diagnosed, treatment and management options can be discussed. These may include lifestyle changes, such as taking regular breaks to rest the hands and wrists, as well as medical treatments, such as physical therapy or surgery. In some cases, treatment may involve a combination of these approaches. By working with a healthcare provider, patients can develop a plan to manage their symptoms and prevent further complications.